
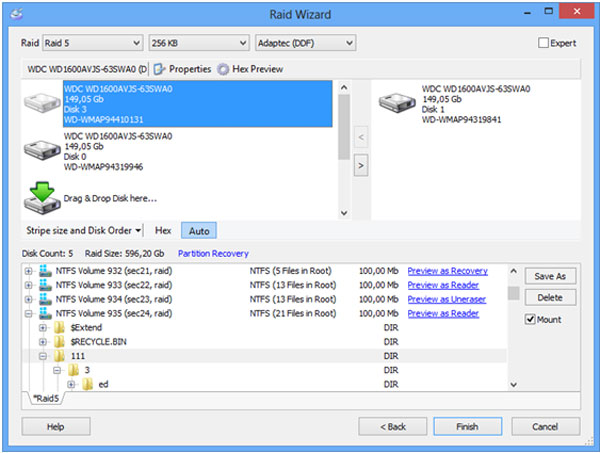
All the intact attached drives will be displayed in the main window on the left. Launch UFS Explorer with administrator’s privileges and modify the program’s settings, if needed.
Install UFS Explorer RAID Recovery and run the software.Hint: You can plug the drives into the motherboard of your PC or сonnect the disks externally using a USB to SATA/IDE adapter. The number of disks which can be missing is equal to the one of the respective level of conventional RAID: zero drives for Btrfs-RAID 0, one drive for Btrfs-RAID 5, two drives for Btrfs-RAID 6, one drive (in some cases two) for Btrfs-RAID 10 and at least one drive out of a mirror must be present in Btrfs-RAID 1. Attach all the available components of your Btrfs-RAID to the PC.Ĭonnect the disks which form the storage to your computer.Rely on the following instruction to perform the procedure: However, if at least one of the copies is intact, UFS Explorer RAID Recovery is able to interpret the Chunk Table and automatically reconstruct Btrfs-RAID of any complexity for further data recovery manipulations. This makes the system much more flexible, but renders it impossible to establish the location of data blocks in case of damage or loss of the two copies of the Chunk Table. In contrast, Btrfs arranges data blocks on the RAID disks in an arbitrary order and keeps track of the correspondence between the blocks and physical addresses on the disk to which they are assigned with the help of a special Chunk Table. Standard RAID is usually handled in two separate steps – the reconstruction of RAID configuration and work file system elements, while the disk space gets divided by the file system into a consecutively numbered set of data blocks, so determining the location of the first bock and the block size is enough to obtain the location of other ones. Speaking of the recovery of files lost from Btrfs-RAID, the specifics of data placement on it makes the restoration process far more complicated.

Hint: All the basic concepts related to RAID are explained in the peculiarities of data organization on RAID. Yet, it is important to understand that Btrfs, although significantly improves the safety of the stored data, cannot entirely prevent its loss. Basically, this file system alone is able to replace the traditional Linux volume management and the mdadm software RAID tool: one can create Btrfs on top of many devices while giving it the fault-tolerance capabilities of RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10. Btrfs as a new-generation file system has incorporated a whole lot of advanced features that enable its great resilience, instant repair of logical errors and simplified administration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
